Chapter 6 - The Caribbean
Genealogists' Guide to North America
Table of Contents
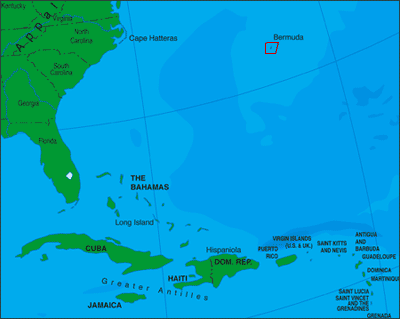
Part 1 - The Florida Keys and Bermuda
Part 2 - Islands of the Caribbean
 Source: About.com - Caribbean Travel
Source: About.com - Caribbean Travel
There are many islands in the Caribbean with significant human population. There are thousands of small islands and keys, many uninhabited. In addition, The State of Florida Contains the Florida Keys and the Dry Tortugas that lie about 67 miles west of Key West. The Dry Tortugas are a small group of islands designated as a National Park and inhabited only by a group of about 15 National Park personnel.
#Part 1 - The Florida Keys and Bermuda
# Source: Miles Media Group, Inc.
Source: Miles Media Group, Inc.
The Florida Keys consists of 1700 small islands, most of which are not inhabited. 800 of these keys are mapped and about 30 are inhabited. Whereas most of the Caribbean Islands are volcanic in origin, the Florida Keys are exposed portions of an ancient coral reef. Most keys are only accessible by boat such as those in Biscayne National Park. The inhabited islands are accessible via an overseas highway extending as a series of bridges from the Florida mainland south of Miami.
The Florida Keys (from the Spanish word Cayo, meaning small island) were first charted in 1513 by Juan Ponce de Leon. Until the completion of an overseas railway in 1910, the islands were only accessible by water. The Spanish had settlements on the keys, but United States settlers did not start appearing until the 1800’s. During the American Civil War, the Florida Keys were part of the Confederacy.
The following is a list of the inhabited islands in the Keys, starting with those in Miami-Dade County and ending at Key West in Monroe County: These are islands that have residences. Although inhabited, some of these keys are private owned and restricted to residents only. Some keys, although accessible, are not included because they have businesses such as fast food and service stations or provide road access to other keys, but have no permanent residents.
- Key Largo was settled sometime before 1870 when a Post Office was built on the island.
- Plantation Key
- Windley Key (Part of the Village of Islamorada)
- Tea Table Key (Part of the Village of Islamorada)
- Upper Matecumbe Key (Part of the Village of Islamorada)
- Lower Matecumbe Key (Part of the Village of Islamorada)
- Islamorada Key
- Craig Key
- Fiesta Key
- Long Key (the city of Layton is located on Long Key)
- Conch Key
- Duck Key
- Knights Key (Part of the City of Marathon)
- Grassy Key (Part of the City of Marathon)
- Key Vaca (Part of the City of Marathon)
- City of Marathon consists of a number of small keys, some uninhabited
- No Name Key
- Big Pine Key
- Little Torch Key
- Ramrod Key
- Summerland Key
- Sugerloaf Key
- Saddlebunch Keys. These are a series of mangrove islands. Bay Point and Bluewater Key are the only inhabited islands in the Saddlebunch Keys.
- Shark Key
- Geiger Key
- Big Coppitt Key
- Boca Chica Key
- Raccoon Key contains the community of Key Haven
- Stock Island (a portion of the Island is part of the City of Key West)
- Fleming Key (Part of the City of Key West but also part of the Key West Naval Air Station and only accessible to military personnel)
- Dredgers Key (Sigsbee Park) is part of the Key West Naval Air Station and has a population of military and civilian employee families. It is an artifical key created from material dredged to make seaplane runways in the shallow bay.
- Sunset Key (Part of the City of Key West)
- Key West was originally known as Cayo Hueso, which means Bone Island. Even though the British took control of Key West in 1763, it was not permanently settled. After the American Revolution it reverted to Spanish control . In 1822, Matthew Perry claimed Key West for the United States. Permanent settlement took place beginning in 1829. Most of the settlers were from the Bahamas. These were the children of British Loyalists who fled from the United States after 1776. Their descendants still live there in an area of the island known as Bahama Village in Old Town.
Bermuda  is not within the Caribbean, nor with any other area of this publication. For research purposes, I have included in this chapter. Bermuda is located in the Atlantic Ocean off the eastern coast of the U.S., 640 miles east-southeast of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina. It is now part of the British Overseas Territory.
is not within the Caribbean, nor with any other area of this publication. For research purposes, I have included in this chapter. Bermuda is located in the Atlantic Ocean off the eastern coast of the U.S., 640 miles east-southeast of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina. It is now part of the British Overseas Territory.
| Bermuda | 1612 | British |
Source: Island Brides.com
#Part 2 - Islands of the Caribbean
Most of the Caribbean Islands were formed by volcanic activity. They lie in a region of intense seismic activity, which includes frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
European contact began with the voyages of Christopher Columbus who first landed in the Bahamas in 1492. The Portuguese and Spanish began claiming territories. Gold, sugar cane, rum and other riches available in this area made it an area of European conquest, war, and exploitation for centuries. England, France and the Netherlands also established colonies to gain economic advantage. The Spanish in particular enslaved the native population nearly to the point of extinction. All of the European nations imported slaves from Africa to work the plantations in their colonies. Since there are thousands of islands, most are either uninhabited or have been settled recently. The presence of fresh water has always been a deciding factor, and with today's power boats available to bring water in on demand many small islands have private ownership or are used as research stations and lighthouses.
The following lists inhabited islands of the Caribbean, showing what countries colonized them. Dates are provided, along with changes in ownership, treaties, independence and current status to help Family Historians with ancestry in this area.
#The Bahamas are in the British Overseas Territory and consist of more than 3000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean South of Florida. Source: Ezilon Maps
Source: Ezilon Maps
#Turks and Caicos.
 Turks and Caicos. I have included East Caicos. It once had a population but has been uninhabited since the early 1900's. These islands are part of the British Overseas Territory and are located at the southern end of the Bahamas Archipelogo.
Turks and Caicos. I have included East Caicos. It once had a population but has been uninhabited since the early 1900's. These islands are part of the British Overseas Territory and are located at the southern end of the Bahamas Archipelogo.
| East Caicos | 1783 | British |
| Middle Caicos | 1783 | British |
| North Caicos | 1783 | British |
| Providenciales | 1783 | British |
 Belize
Belize  Nicaragua
Nicaragua  Mexico
Mexico  Panama
Panama  Honduras
Honduras
| Ambergris Caye | 1848 | British | Belize |
| Corn Islands | 1655 | British (1971 turned over to Nicaragua) | Nicaragua |
| Cozumel | 17th Century | Spanish | Mexico |
| Isla Mujeres | 17th Century | Spanish | Mexico |
| Bastimentos Island | 16th Century | Spanish | Panama |
| Colón Island | 16th Century | Spanish | Panama |
| Popa Island | 16th Century | Spanish | Panama |
| Solarte Island | 16th Century | Spanish | Panama |
| Guanaja | 16th Century | Spanish | Honduras |
| Roatan | 16th Century | Spanish | Honduras |
| Útila | 16th Century | Spanish | Honduras |
| #South American Caribbean. Providencia was claimed by Spain, Argentina, Nicaragua and Columbia at various times. |
| Coche Island | 1800's | Spanish | Venezuela |
| Isla Margarita | 1498-1914 | Spanish | Venezuela |
| Providencia | 1630 | British (1803-1912) Columbia since 1912 | Columbia |
| San Andrés | 1627 | British (Spanish since 1792) | Colombia |
Greater Antilles - Dominican Republic (part of Island of Hispaniola)
| Dominican Republic | 1821 Independent |
Greater Antilles - Haiti (part of Island of Hispaniola)
| Haiti | 1804 | Independent | Republic of Haiti |
| Gonâve Island | 1697 | Spanish | Republic of Haiti |
| Île à Vache Island | 1697 | Spanish | Republic of Haiti |
| Tortuga | 1697 | Spanish | Republic of Haiti |
Greater Antilles - Jamaica
| Jamaica (Spanish Santiago) | 1509 | Spanish (British 1655) (1962 Independent) |
Greater Antilles - Cayman Islands. Now part of the British Overseas Territory
| Cayman Brac | 1661 | British |
| Grand Cayman | 1661 | British |
| Little Cayman | 1661 | British |
Greater Antilles - Cuba. The Republic of Cuba is the largest island in the Caribbean and is located 90 miles south of Key West Florida.
| Cuba | 1511 | Spanish (1902 Independent) | Republic of Cuba |
| Cayo Coco | 1511 | Spanish | Republic of Cuba |
| Cayo Fragoso | 1511 | Spanish | Republic of Cuba |
| Cayo Guajaba | 1511 | Spanish | Republic of Cuba |
| Cayo Guillermo | 1511 | Spanish | Republic of Cuba |
| Cayo Largo del Sur | 1511 | Spanish | Republic of Cuba |
| Cayo Romano | 1511 | Spanish | Republic of Cuba |
| Cayo Sabinal | 1511 | Spanish | Republic of Cuba |
| Cayo Saetia | 1511 | Spanish | Republic of Cuba |
| Isla de la Juventud | 1511 | Spanish | Republic of Cuba |
#Lesser Antilles (also known as the Caribbees) are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Caribbean Sea. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America. The Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles compose the Antilles, which are in turn part of the West Indies along with the Bahamas, the Cayman Islands, and the Turks and Caicos Islands. The islands of the Lesser Antilles are divided into three groups. The Windward Islands in the south, the Leeward Islands in the north, and the Leeward Antilles in the west consisting of islands just off the coast of Venezuela.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lesser_Antilles
Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: Independent Nations
| Antigua | 1632 | British (1981 Independent) | Antigua and Barbuda |
| Barbuda | 1685 | British (1981 Independent) | Antigua and Barbuda |
| Barbados | 1627 | British (1966 Independent) | Barbados |
| Nevis | 1628 | British (1983 Independent) | Saint Kitts and Nevis |
| Saint Kitts (Saint Christopher) | 1623 | British (1625 French) (1983 Independent) | Saint Kitts and Nevis |
Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: French Overseas Region (F.O.R.)
Saint Martin is the smallest Island in the world to be split between two countries, Saint Martin belonging to France, and Sint Maarten to the Netherlands. Saint Martin officially flies the French Tricolor, but has a collective flag also. Îles des Saints, La Désirade and Marie Galante all fly the flag of Guadeloupe an unofficial flag. All officially fly the French Tricolor.
| Saint Barthélemy (Saint Barts) | 1623 | French (1946 F.O.R.) |
| Saint Martin | 1648 | French (2003 F.O.R.) |
| Guadeloupe-Grande-Terre | 1635 | French (1946 jF.O.R.) |
| Guadeloupe-Terre-de-Bas | 1635 | French (1946 F.O.R.) |
| Guadeloupe-Terre-de-Haut | 1635 | French (1946 F.O.R.) |
| Îles des Saintes | 1649 | French |
| La Désirade | 18th Century | French |
| Marie Galante | 1648 | French |
Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: Kingdom of the Netherlands (K.O.N)  Aruba
Aruba  Bonaire
Bonaire  Curacao
Curacao
| Aruba | 1508 | Spanish (Dutch since 1836) |
| Bonaire | 1621 | Dutch |
| Curaçao | 1600's | Dutch |
| Saba | 17th Century | Dutch |
| Sint Eustatius | 1600's | Dutch |
| Sint Maarten | 1648 | Dutch (2010 K.O.N.) |
Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: British Overseas Territory
| Anguilla | 1650 | British |
| Montserrat | 1632 | British |
The British Virgin Islands consists of over 50 islands and cays, about 15 inhabited.
British Virgin Islands
Part of British Overseas Territory
Anegada
1672
British
Jost Van Dyke
1672
British
Tortola
1672
1648 Dutch - British since 1648
Virgin Gorda
1672
British
Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: Puerto Rican Virgin Islands
Puerto Rico and its islands are an unincorporated territory of the United States.
Puerto Rico
17th Century
Dutch (1898 U.S. Protectorate)
Culebra
1880
Spanish (1917 Independent Municipality)
Isla Mona
15th Century
Spanish
Isleta de San Juan
15th Century
Spanish
Vieques
1811
Spanish
Lesser Antilles Leeward Islands: United States Virgin Islands
The U.S Virgin Islands were acquired by the United States in 1917 and are classified as United States Protectorates.
| United States Virgin Islands | (1917 U.S,) | |
| Saint Croix | 1650 | French (1713 British) (1917 U.S,) |
| Saint John | 1718 | Danish (1917 U.S,) |
| Saint Thomas | 1672 | Danish (1917 U.S,) |
| Water Island | 1917 | Danish (1917 U.S,) |
Lesser Antilles Windward Islands: Independent Nations
Dominica
1673
British (1715 French) (1978 Independent)
Commonwealth of Dominica
Saint Lucia
1643
French (1814 British) (1979 Independent
Saint (Santa) Lucia
#Windward Islands - The Grenadines
The Grenadines are windward islands, but they lie south of the boundary of the Lesser Antilles. This chain consists of two large islands, Saint Vincent to the north and Grenada to the south with a series of small islands between. There are over 600 islands total, most of which are uninhabited. The small islands are divided between ownership, part to Saint Vincent and part to Grenada. Saint Vincent with its islands is the country of "Saint Vincent and the Grenadines". Grenada and its islands are the country of "Grenada".
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
These islands, along with Saint Vincent, make up the Grenadines Parish
- Young Island
- Bequia
- Petit Nevis
- Isle à Quatre
- Bettowia
- Baliceaux
- Mustique
- Petit Mustique
- Savan
- Petit Canouan
- Canouan
- Mayreau
- Tobago Cays
- Union Island
- Petit Saint Vincent
- Palm Island
- Mopion
Carriacou and Petite Martinique are dependencies of Grenada.
- Carriacou 34 km2 (13 sq mi), 7,400, Capital Hillsborough
- Petite Martinique 3.7 km2 (910 acres), 550, Capital North Village
- Related Topics